Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is the process of developing prototypes for products as fast as possible.
In this guide we’ll cover the forms of rapid prototyping, its applications and its importance.
Table of Contents
Prototyping is an integral part of product development. It’s where design teams create an experimental product to apply their ideas.
Problem: Functional prototypes often requires similar processes and resources to producing finished products. Traditional production processes like CNC machining or injection molding are expensive and slow. These need tools acquisition and setup; hence making custom prototyping expensive and slow.
Solution: Rapid or fast prototyping aids organizations in transforming ideas into real products. It helps turn concepts into quality prototypes that look like finished products. Engineers and product designers can develop prototypes from computer-aided design (CAD) data faster. They can also apply quick changes on their designs based on the feedback acquired.

Rapid Prototyping Definition
It is the process of developing prototypes as fast as possible to emulate a final product design. It is a series of techniques used to model a scale prototype of a physical component or an assembly using CAD data.
Designers usually complete the process using additive manufacturing or 3D printing. Compared to traditional subtractive methods, additive manufacturing does not need tooling. It offers you an almost unlimited type of freedom in fabricating prototypes.

Different Types of Rapid Prototyping
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA was the first successful technique used for commercial 3D printing. It is a rapid prototyping process that is fast and less costly. It uses solidified photosensitive liquid to develop a prototype design, layer by layer. The liquid is often solidified using a computer-generated UV light.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS helps in both plastic and metal prototyping. With the help of a powder bed, it builds a prototype layer-by-layer, using a laser to heat and sediment the powdered substance. However, the prototyped parts are not as strong as those produced by stereolithography. The surface of your final product is often rough and might need some more work to make it presentable.
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
FDM is a less expensive and easy-to-use process. It’s found in most non-industrial 3D desktop. A spool of thermoplastic filament is melted and the resulting liquid is layered to create a 3D design. During the early times of use for 3D printing, FDM resulted in weak resolute designs. But, the process is improving, making it ideal for product development.
Binder Jetting
Binder jetting technique enables you to print one or more parts at once. Even so, the parts created are not strong enough compared to those from the SLS. Like SLS though, this process involves the use of a powder bed to layer the prototyped parts.
You can read more information about rapid prototyping with 3d printing here.
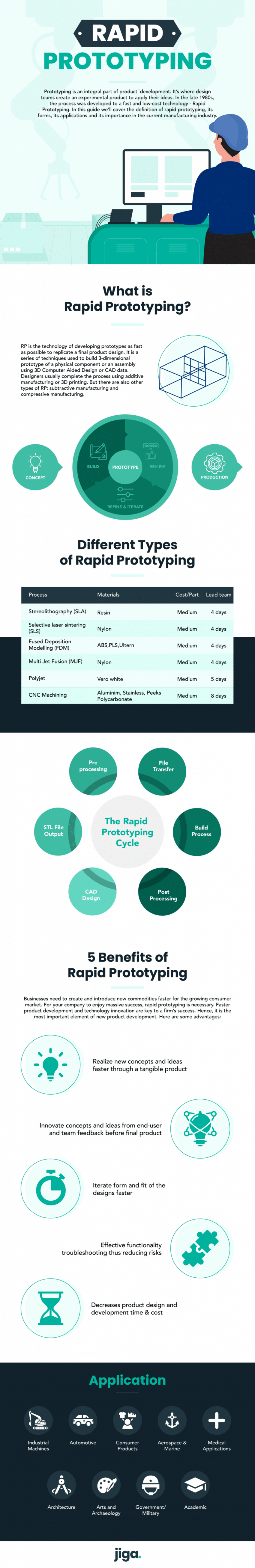
Importance of Rapid Prototyping
Businesses need to create and introduce new commodities faster for the growing consumer market. For your company to enjoy massive success, rapid prototyping is necessary. Faster product development and technology innovation are key to a firm’s success. Hence, it is the most important element of new product development. Here are some advantages:
Realize and Explore New Concepts Faster
Rapid prototyping enables you to apply new concepts and ideas into an experimental model faster. You will also be able to understand the appearance and feel of the prototype design in real life.
Communicate Ideas Effectively
Rapid prototyping allows you to get precise and useful user feedback. This is important to help you understand what the user need and want. You can then restructure and refine your designs effectively. A rapid prototype model helps designers and engineers to visualize their ideas to the relevant people.
Design Iteratively and Instantly Incorporate Changes
Prototyping goes through testing, assessment, and polishing before obtaining a finished product. Rapid prototyping allows for flexibility in creating more realistic prototypes. It also enhances the instant implementation of changes in prototype products.
Applications of Rapid Prototyping
Companies use rapid prototyping to test size and fit of products before moving to mass production.
This technique was used to develop scale models and physical parts for the automobile industry. But, the technique has been adopted across multiple industries like aerospace, and the medical sector.